Introduction: Today's Changing Software
Environments
Change is a constant factor in today's software environments.
Software engineers have to worry about changing operating systems,
libraries, and tools, not to mention the code modules they are
responsible for and those with which their software interacts.
Inability to deal with changes in a software project leads to
needless delays and avoidable rework. Ironically, the answers to
these questions do exist but are not readily captureable.
Most organizations don't have the time to address these issues.
Those engineers and managers that do tackle these problems typically
develop ad hoc, creative solutions that are temporary, limited, not
extensible to other parts of the organization, and are simply
another form of change with which the poor developers must contend. If change is not
managed, it can be disastrous to an organization's technology and
to its employees.
Huge Software Projects
Not only is the software development environment changing rapidly,
but it is becoming increasingly complex, in both size as well as in
process. For example, the development of the Space Station created
a 3X increase in just 10 years in millions of object instructions
(Figure 1). And the Space Station hasn't even been launched!
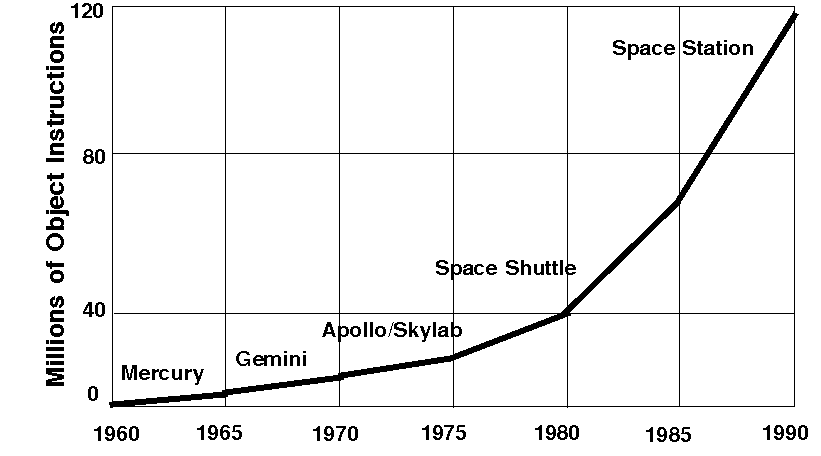
FIGURE 1. Software Size Complexity as Evidenced by the Space Effort
At Silicon Graphics, complexity has also increased at an incredible pace (Figure 2). The
number of interfaces and overall system complexity are an increasing challenge to
manage.
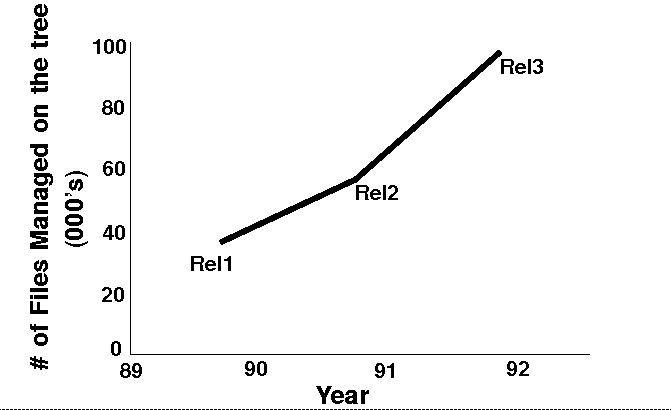
FIGURE 2. SGI's Dramatic Increase in the Size of System Software Releases
Software Management Complexity
It is simplistic, though, to attribute software development problems solely to increasing
size and complexity. The rapidity of the development cycle today adds fuel on the fire.
For instance, in Figure 3, we see a typical configuration management problem. The
mainline of development moves across the top of the drawing. At points during the
process, complete clones (labeled Rel in the figure) are released for development work.
During the course of development, intermediate releases may be fanned out to
numerous developers, who must make their changes and merge them back into the
release version. Eventually changes made to the development release must be merged
back into the mainline. To further complicate the situation, it is not unusual to release
variant versions of the software to various subscribers of the system for trial purposes.
With so many different versions of source files and potentially compilers, linkers, and
build environments, it is easy to see the potential for problems.
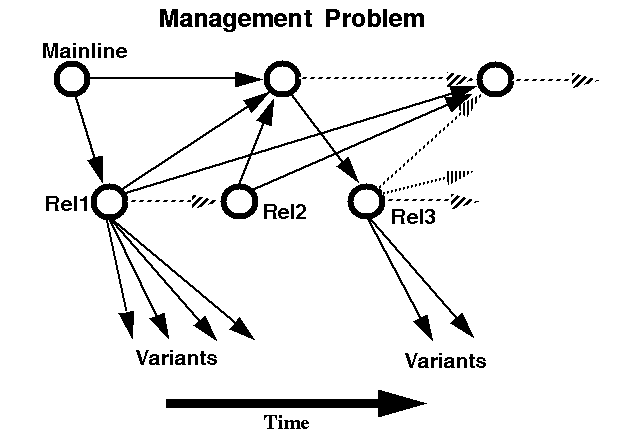
FIGURE 3. A Typical Configuration Problem
Problems with development in this type of environment are numerous. Here are a few:
Difficulty of Developing Multiple Releases in Parallel
This is the classic configuration management problem. Companies, today, must support
current, old and new development lines, and sometimes even variants on each. In fact,
this problem will only get worse, as open system pressures increase.
Time-Consuming System Builds
It is not uncommon to find System Builds that take 36 hours. Build engineers might start
a build on Friday evening and are able to certify the build some time during the day on
Sunday. If a build fails, however, it is common to find builds certified for release on
Tuesday of the following week.
Inability to Fix Older Releases
Many customers do not want to upgrade to the latest release. Thus, we are forced to
support more numbers of releases. We must be able to do this efficiently and accurately.
Uncertain Status of Bugs
It is too difficult to figure out what bugs were fixed in a given release. It is typical to sit
in a system release meeting and find managers and engineers who have to ask other
managers and engineers if a particular bug was fixed in a particular release.
Coordinating change is difficult; finding out what changed is nearly impossible.
Lack of Traceability
It is almost impossible to synchronize process deliverables. At some point in the
lifecycle of a system release, all of the process deliverables should be frozen and
attached to the system release. These include the requirements, designs, sources,
executables, tests (data and results) and bug reports for a given system release. At any
point in the lifecycle, a development or support engineer should be able to trace from
any given executable to any given process deliverable.
Ramifications of Changes
It is hard to figure out what changed or what the impact of a change will be. Too
frequently, engineers ask, "it worked yesterday, why doesn't it work today?" With
today's systems, it is impossible to figure out what changed or to predict the impact of a
new change. Also, almost weekly, engineering managers must make decisions based
upon the potential impact of a change in the system. With today's systems, it is virtually
impossible to answer that question.
Isolating Files with Selected Sharing
It is difficult to set up "sandboxes." One of the fundamental software development
problems is to set up environments so that engineers can effectively share and isolate
their work. Traditionally, scripts are written on top of RCS or SCCS, and through the
use of links and copies, these engineering "sandboxes" are set up. This process is time
consuming and static. Usually engineers are forced to share what they don't want to
share, and are forced to copy what they would rather share. Merging changes becomes a
nightmare.
Managing Change in Software
The answer to managing change lies in our ability to understand, control, and track the
software development environment in its entirety from initial design requirements
through release and maintenance, including development and integration. Gene Forte,
Executive Editor of CASE Outlook, puts it best:
"As we gain a better understanding of these factors, we find that getting control of
all the work products of development, and their relationships to each other and the
development process, is fundamental to the business of Total Quality Management
in software, just as it is in manufacturing and in other engineering fields....
...CM is now charged with managing all the work products involved in software
development: all manner of graphical, textual and symbolic design documents; test
suites and results; metrics; source and object code; system and network options;
data and program locations; business models; and anything else we may invent in
the coming years. The latest automated build facilities no longer execute a fixed
script, but they automatically determine the correct version of source code as well
as the compilers and linkers used to build the system. They know which modules
need recompiling and which do not, and they want user-defined rules for
promoting systems from development to test and then to production.
We are also demanding that CM handle new dimensions of complexity. For
example, we not only want to archive historical versions of a particular
application, we want to be able to go forward or backward through the historical
sequence of versions, and we want to have multiple coexisting variants for parallel
development, for many platform targets and for different market niches. We want
tools to manage these relationships in a way that is transparent to the developer, so
that details of file name and directory variations are of no consequence." - CASE
Outlook 90, No. 2
In addition to the general requirements of version control, configuration management
and system building, the most asked for integrated application is that of problem
tracking and reporting. By integrating a problem tracking system with the CMS facility,
the task of determining which bugs have been fixed and which feature requests have
been implemented in a given release are greatly simplified.